what nat ip address is a public ip address that maps to an inside device?
Discover why Network Address Translation is important, how it works and what different types of NAT are available.
Network address translation (NAT) is a procedure that allows multiple devices on a local network to share a unmarried IP address publicly, fifty-fifty when all devices have unique private IP addresses within that network.
Network address translation facilitates this past converting the assigned private addresses of network devices into the public IP addresses of their respective networks. This means packets of data tin can be sent and received by the correct devices. Without the need for multiple public IPs within a unmarried local network.
Nearly domicile routers utilize network address translation, but this isn't the sole use of NAT. Even big organizations with a relatively large private network may choose to have their entire internal network employ a single IP address for economic or security reasons.
So how does network accost translation take multiple private IP addresses and use merely one public IP address? Permit'due south dig into the process below.
How does network accost translation work?
Before we get into how network accost translation works, first nosotros chop-chop demand to make sure we're on the same folio near what an IP address is and why information technology's important for the exchange of data on the net.
IP addresses part as the mailing addresses of the cyberspace. When data is sent via the internet, it is sent in IP packets, each of which needs a destination accost to know where information technology's meant to get.
Yet, there are different kinds of IP addresses. When discussing network address translation, nosotros mainly talk nigh public and private IP addresses.
A public address is a global IP accost. It is accessible to other devices on the internet, outside of a given LAN network. A individual address is an IP accost assigned to a specific network device. Information technology is accessible only to other devices within the same local network.
Devices with individual IP addresses tin send requests for data. All the same, if the source IP accost remains private, the receiving server can't tell where to return the information dorsum to.
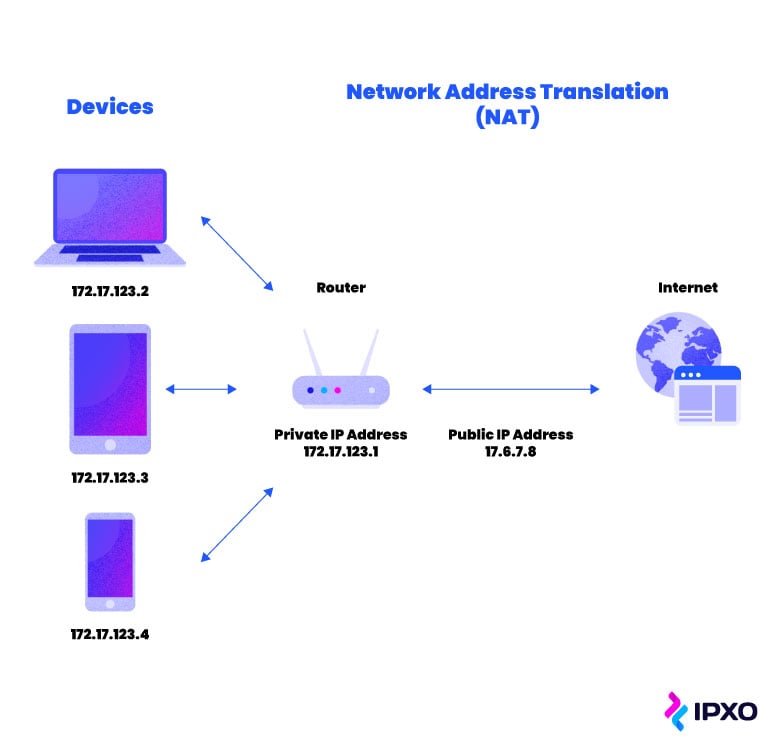
This is where network accost translation comes in. When sending data requests to an external network, a NAT router or NAT firewall is able to convert the device's private IP address into the network's public IP address. This ensures that the data is sent to the right place.
The procedure of network accost translation
Here'due south an case of how network address translation works in practice:
- Y'all connect your device to your home Wi-Fi network.
- Your habitation router assigns your device a individual IP accost. Like all private IP addresses, this address is only used inside your network.
- You try to load a web folio. This sends a request through the cyberspace via your router.
- Your NAT router changes the source address of the asking from your device'south private address to your network'southward public IP address. The translation is saved in a NAT table.
- The server you're attempting to access returns the requested packet to your network's public IP address.
- Your router changes the destination accost back to your device's private IP accost and routes the packet to your device.
Why is network accost translation important?
NAT helps networks in two cardinal means. First, it acts equally a security layer between the public internet and private devices on an internal network. Second, it helps reduce the need for global IP addresses. This is particularly important for IPv4 addresses, as the adoption of IPv6 addresses is still years abroad.
Security purposes
Many network engineers use network accost translation to protect devices on their networks from cyberattacks.
The NAT process acts every bit an additional layer of security betwixt devices on a individual network and the remainder of the internet. Information technology offers the NAT router or NAT firewall the opportunity to sort and cheque the data every bit information technology'southward sent to a device. This tin can assist prevent anyone from accessing a private device.
Let us annotation that your private addresses cannot ensure full security. Without a doubtfulness, you should also employ encryption and other security tools. That said, keeping your devices on a local IP address is a skillful actress security measure.
Individual IP exhaustion prevention
Using a single public IP accost for multiple devices on a network likewise helps ensure that the assignment of public IPs is as efficient every bit possible.
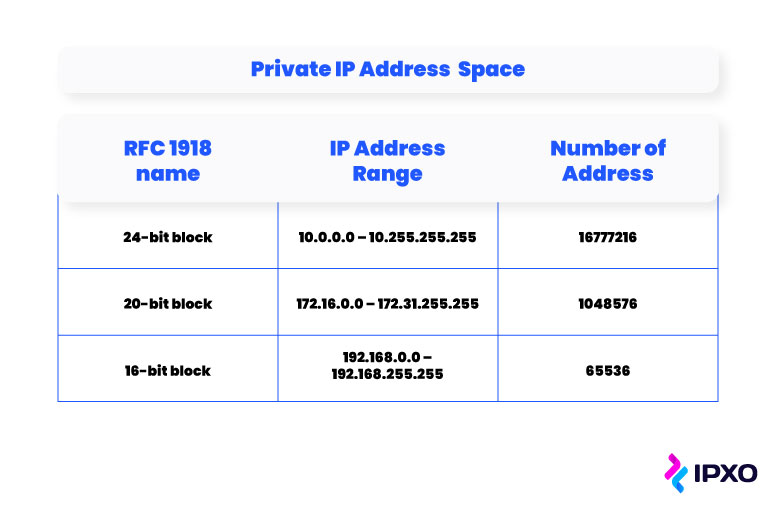
The problem being solved here is that IPv4 is still the well-nigh commonly used format of IP addresses on the internet. However, there are only almost 4.3 billion possible IPv4 addresses available, and nosotros are already dealing with IPv4 exhaustion.
If each device on all individual IP networks was assigned a public IP accost, we'd very apace run out of assignable IPv4 addresses. This is why, instead of assigning a public IP address, information technology's useful to be able to assign local IP addresses inside a network and use only one global IP address for all traffic on that network.
Finer, you're accumulation the traffic on an entire network to a single source IP address. You lot then use publicly unregistered IP address identifiers for devices within the network.
Types of network address translation
Since network address translation exists within the world of IP addresses, it'll come equally no surprise that at that place's the added complexity of there being multiple kinds of NAT. There are, in fact, three.
If yous know anything nigh IP addresses, you may also know that they autumn into ii other categories: static and dynamic addresses. These correspond to the first two kinds of NAT.
Static IP addresses utilise the aforementioned address over time, whereas dynamic IP addresses change periodically. Learn more nigh both below.
Static NAT (SNAT)
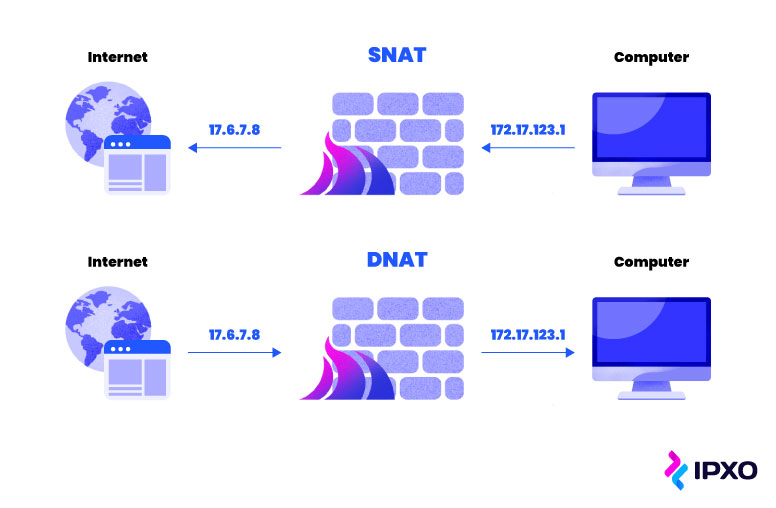
Static network accost translation refers to NAT that uses a consistent public IP address each time it translates a private IP address to a public one. The static refers to the fact that the global IP address remains unchanged with each translation.
In the example of static network accost translation, all private, unregistered IP addresses on a network are mapped to specific public addresses. This means that each device on the network is associated with a specific public address.
This is a NAT solution oft used in web hosting. It is rarely used by big organizations, as information technology would crave the arrangement to buy a public IP address for every connected device.
Dynamic NAT (DNAT)
As you may have guessed, dynamic network address translation differs from static NAT. That is because it uses different IP addresses rather than the same ane each time.
Under dynamic NAT, the router or firewall running the NAT (i.e., NAT device) has access to a pool of public IP addresses. When translating a individual address to a public 1, dynamic NAT allows routers to cull whatsoever free public IP address from the puddle.
As a result, the NAT device uses a dissimilar IP address for each translation. This means that you can't predict which global address each individual address is mapped onto.
While this is a bully solution for using IP addresses efficiently, it'south too relatively costly for organizations to configure NAT. That is considering they need to invest in a big enough pool of publicly registered IP addresses.
Although this means that more devices tin can connect to the internet on a network, the number of packets sent and received at any given time is still express past the number of public IP addresses bachelor. If the puddle has 15 public IPs, and so only 15 local IPs can be translated at any given moment.
Port address translation (PAT)
The final form of NAT is port address translation, which is sometimes referred to every bit NAT overload. This is a blazon of dynamic NAT, but it differs in a few key ways.
Instead of each private IP address beingness mapped onto a single unique IP address (public), several private IP addresses are banded together to use one public IP accost.
So, instead of using the IP addresses to place the source device, the router or NAT firewall uses port numbers to distinguish the traffic. These port numbers are assigned to devices on the network. They allow the router to return packets to multiple devices using a single public IP.
NAT overload is the almost cost-effective grade of NAT. Information technology requires the smallest number of public IP addresses to be registered by an organization. In theory, thousands of devices connected to a network tin all access the internet using the same public IP accost.
What is the difference betwixt DNAT and SNAT?
The key difference between dynamic and static NAT is how individual IPs are mapped onto public ones.
In the static version, IPs are mapped ane to 1 from private or to public. This means that each individual device always uses the aforementioned public address.
In the case of dynamic NAT, the publicly mapped IPs are fatigued from a pool when they're needed. This means a private device has a different public IP each time it accesses the internet.
Large organizations commonly use both, and both require investment in global IPs.
Conclusion
To sum up, network address translation (NAT) is a way for a network to utilise the same IP address for multiple connected devices.
Though every device has its own local IP address, these are unregistered IP addresses. Internal IP addresses demand to be translated into global addresses and so that the IP bundle of data beingness requested can be returned to the correct device.
A NAT gateway router or firewall is able to carry out this translation each style. It does this either statically, using the same public IP for a specific individual IP, or dynamically, assigning public IPs to private ones from a puddle.
All this can help networks relieve money, heave security and ensure more public IPs bachelor for apply.
alexanderandee1958.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.ipxo.com/tutorial/what-is-nat/
0 Response to "what nat ip address is a public ip address that maps to an inside device?"
Post a Comment